Students entering Medical Physics specialisation are required to have completed courses in mathematics and physics, laboratories common for all specialisation and following courses:
Numerical methods I & II
Computer programming I & II
Quantum mechanics I
Introduction to nuclear physics and elementary particles
Electrodynamics of media
Introduction to biophysics
Physical methods of environment research
Laboratory of Medical Physics - lectures
lectures+pract. classes
| SEMESTER: | VII | VIII | IX | X | XI |
| Fundamental problems of biomedical sciences | 2 | ||||
| Physical foundations of medical diagnostics | 2+2 | ||||
| Statistics and signal analysis | 2+2 | 2+2 | |||
| Laboratory of medical physics* | 6 | 6 | |||
| Bioelectricity and elements of biocybernetics | 2 | 2 | |||
| Physical foundations of radiotherapy and radioprotection | 2+1 | ||||
| Mathematical modelling in biology and medicine | 2+2 | ||||
| Biochemistry | 2 | ||||
| Radiometry and radioecology | 2 | ||||
| Master's thesis preparation | |||||
| Medical physics seminar | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| The Warsaw Medical University | Akademia Medyczna w Warszawie |
| Medical Physics Department, Maria Skłodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Centre and Institute of Oncology | Instytut Onkologii, Zakład Fizyki |
| Center for Medical Postgraduate Studies | Centrum Medycznego Kształcenia Podyplomowego |
| Central Laboratory for Radiological Protection | Centralne Laboratorium Ochrony Radiologicznej |
Bioelectricity and elements of biocybernetics
1. Ionic phenomena in nervous and muscle cells. Hodgkin-Huxley theory.
2. Propagation of nervous excitation. Synaptic conductivity and potentials.
Transmissions in neural ensembles.
3. Electrical phenomena in muscle cells. Muscle control.
4. Electrical phenomena in sensory organs. Active stimulus transduction.
5. Volume conductivity. Tissue's electrical properties.
6. Elements of stochastic signal analysis.
7. Generation, registration and analysis of electric and magnetic signals:
EEG, EP, EMG, ERG, EOG, EDG, MEG, MKG
8. Modelling of neuron's population activity. Freeman's theory.
9. Artificial neural networks. A formal neuron. Perceptron and Adaline.
Model of associative memory - Hopfield network. Multilayer networks and
error backpropagation. Supervised and unsupervised learning.
Physical foundations of radiotherapy and radioprotection
1. Basics of interaction of ionizing radiation, used in radiotherapy
of cancers, with ph. matter
2. Basics of dosimetry of ionizing radiation used in radiotherapy
3. Forming of external therapeutic beams of photons and electrons:
Roentgen apparatus,
Co-60 sources, medical linear accelerators of electrons
4. Distributions of therapeutic dose, external beams of ionizing radiation:
dependence of dose's distribution in phantom on physical beam's parameters,
distribution in non-uniform media
5. Basic techniques of irradiation with external beams of electrons
and photons; exercises in using computer system for teleradiotherapy planning
6. Radiobiological bases of ionizing radiation applications for therapeutic
purposes, linear-quadratic model
7. Physical foundations of brachytherapy
Statistics and signal analysis
1. Statistics: definitions of probability, density function, variance.
Distributions: Gauss, uniform, binomial, Poisson, chi-square, Central Limit
Theorem. Estimation. Maximum Likehood method. Verification of statistical
hypotheses. Correlation coefficient, covariance matrix. ANOVA, MANOVA,
chi-square test of goodness of fit, Cluster Analysis, Principal Components
Analysis, Factor Analysis, Discriminant Analysis, non-parametric tests
2. Signal analysis: computability, notion of alghoritm's numerical
complexity - notation O(.). NP-hard and NP-complete problems. Binary
representations of characters, numbers, images etc. Hilbert space L^2(0,
2 pi). Set of vectors: linearly independent, orthogonal, basis. Fourier
coefficients. Isomorphism of L^2 and l^2. Difference between Fourier integral
and Fourier series. Frequency domain filtering. AR and ARMA models. Time-frequency
phase space. Wavelet analysis. Matching Pursuit.
Biochemistry
1. Features of a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
2. Proteins: I-, II-, III- and IV-order structure
3. Enzymes
4. Structure of lipids and carbohydrates
5. Krebs cycle
6. Biological oxygenation - foundations of bioenergetics.
7. Photosynthesis
8. Nucleic acids - structure and functions.
9. DNA and RNA viruses, HIV virus.
10. Membranes - structure and chemical compound
11. Process of vision - structure of the eye, retina etc.
12. Muscle contraction. Structure of a skeleton muscle.
13. Metaboism regulation.
14. Regulation via nervous system
Fundamental problems of biomedical sciences
This lecture presents in a contemporary and synthetic form basic elements
of construction and functions of the human organism. Description involves
diverse structural levels, beginning with molecular and cellular through
tissues, organs and systems until the organism as a whole. Particular attention
is paid to dependencies connecting proper and pathological phenomena on
different levels, esp. as related to regulatory processes and their disfunctions.
Physical foundations of medical diagnostics
1. Physical problems in radiodiagnostics
2. Diagnostic examination techniques
3. Imaging equipment and its physical parameters
4. Computer Tomography and Roentgen diagnostics and nuclear medicine
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
6. Sources of radiation: RTG lamps and radiopharmaceutic drugs
7. Radiation detectors
8. X-rays and gamma radiation in biological objects
9. Imaging methods in medical diagnostics
10. Data processing in qualitative diagnostics and presenation
11. Statistical methods in imaging techniques
12. Evaluation of diagnostic images quality
13. Dosimetry of radiation and equipment used in medical diagnostics
14. Patient's exposure to ionizing radiation
15. Radioprotection in sites applying ionizing radiation
16. Quality control of diagnostic equipment operation
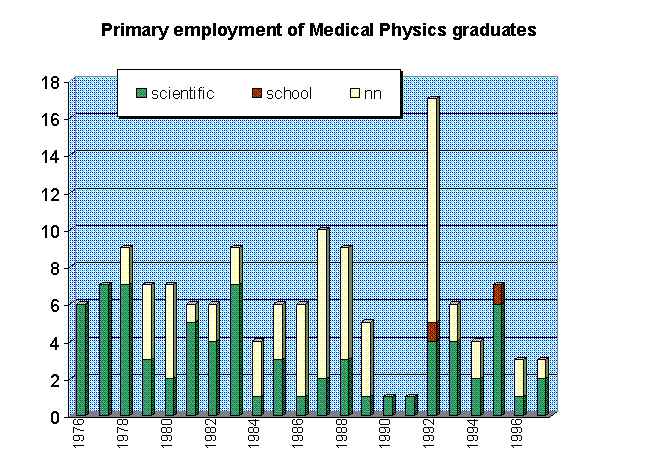
Laboratory of Medical Physics - employment of graduates
The following institutions closely cooperate with Lab. Med. Physics and employ our graduates; in many cases students make first contacts during Medical Physics Laboratory assignments on VII and VIII semesters:
| The Warsaw Medical University | Akademia Medyczna w Warszawie |
| Medical Physics Department, Maria Skłodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Centre and Institute of Oncology | Instytut Onkologii, Zakład Fizyki |
| Center for Medical Postgraduate Studies | Centrum Medycznego Kształcenia Podyplomowego |
| Central Laboratory for Radiological Protection | Centralne Laboratorium Ochrony Radiologicznej |
| Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology | Instytut Biologii Doświadczalnej im. Nenckiego |
| Institute of Biocybernetics | Instytut Biocybernetyki |
| IPPT Institute | Instytut Podstawowych Problemów Techniki |
| Inst. Biochemistry and Biophysics, Polish Acad. of Science | Instytut Biochemii i Biofizyki PAN |
| Institute of Psychoneurology | Instytut Psychoneurologii |
| Military Medical University | Wojskowa Akademia Medyczna |
|
Military Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology | Wojskowy Instytut Higieny i Epidemiologii |

"Primary" means here the first one after graduating; of the above at
least six persons we know about changed job for better paid non-scientific
companies.
Members of Society of Students of Medical Physics launched a questionnaire-based
survey aimed at foreign and private comapnies of related profile, containing
questions about employment possibilities, also for B.Sc. graduates.