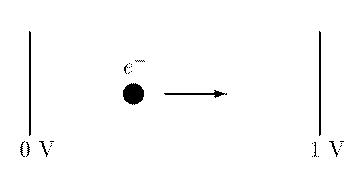
When an electron passes through a potential difference of 1 volt, the energy it acquires is called 1 eV. If the average energy of all particles in a gas was 1 eV, it will correspond to a temperature of 10 000 degrees Kelvin.
Televisions are small scale particle accelerators. But they use the same basic principles as a large accelerator like LEP at CERN.
- The source of electrons is a hot filament.
- Electrons are accelerated towards and through a positively charged electrode.
- Electromagnetic fields then sweep the beam across the screen and builds up a picture.