

Next: Spherical symmetry
Up: The Skyrme Hartree-Fock-Bogolyubov equations
Previous: The Skyrme Hartree-Fock-Bogolyubov equations
In the Skyrme-HFB formalism,
the evaluation of the expectation value of the energy leads
to an expression which is a functional of the local densities,
namely, the particle (normal) and pairing (abnormal) densities
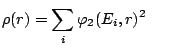 and and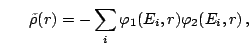 |
(4) |
and their derivatives.
The presence of non local terms in the force leads
to a dependence on the normal and abnormal kinetic densities
while the spin-orbit term leads to a dependence on the
spin current tensors
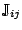 and
and
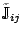 .
We do not give here the definitions of these tensors, because for the
spherical symmetry discussed here
they reduce to the corresponding spin
current vectors
.
We do not give here the definitions of these tensors, because for the
spherical symmetry discussed here
they reduce to the corresponding spin
current vectors
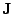 and
and
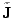


Next: Spherical symmetry
Up: The Skyrme Hartree-Fock-Bogolyubov equations
Previous: The Skyrme Hartree-Fock-Bogolyubov equations
Jacek Dobaczewski
2005-01-23