


Next: Fermi surfaces and kinetic
Up: Infinite Nuclear Matter
Previous: Introduction
The four basic degrees of freedom of homogeneous INM are the
isoscalar scalar density
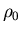 ,
the isovector scalar density
,
the isovector scalar density 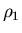 ,
the isoscalar
vector density s0, and the isovector vector density s1.
They can be expressed through the usual neutron and proton,
spin-up, and spin-down densities in the following way.
,
the isoscalar
vector density s0, and the isovector vector density s1.
They can be expressed through the usual neutron and proton,
spin-up, and spin-down densities in the following way.
Similarly, densities of protons and neutrons
with spin up and down can be expressed as:
where
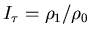 is the relative isospin excess,
is the relative isospin excess,
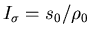 is the relative spin excess, and
is the relative spin excess, and
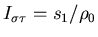 is the relative spin-isospin excess,
with
is the relative spin-isospin excess,
with
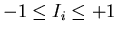 .
.
In symmetric unpolarized INM Ii = 0, while in asymmetric INM
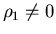 .
Polarized INM has
.
Polarized INM has 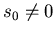 ,
and
spin-isospin polarized nuclear matter has
,
and
spin-isospin polarized nuclear matter has 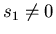 .
.



Next: Fermi surfaces and kinetic
Up: Infinite Nuclear Matter
Previous: Introduction
Jacek Dobaczewski
2002-03-15
![]() .
Polarized INM has
.
Polarized INM has ![]() ,
and
spin-isospin polarized nuclear matter has
,
and
spin-isospin polarized nuclear matter has ![]() .
.