- ... Blinowska
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- Laboratory
of Medical Physics, Institute of Experimental Physics, Warsaw
University, ul. Hoza 69, 00-681 Warszawa, Poland,
http://brain.fuw.edu.pl.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... (Hz)
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- For
the angular frequency this constant would be equal to
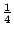
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
expansion
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- In practice this sum will be of course finite; in
this study we used 2 different stopping criteria: for the Dataset I
iterations were stopped when 99.9% of signal's energy was explained,
which resulted in about 400-500 waveforms per trial. For the Dataset
II number of iterations was fixed at 1300. These criterions were chosen to ensure proper repreentation of high frequency structures at a minimum computational cost (number of iterations. Details of the MP procedure can be found in [14]
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
stationarity.
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- Standard test for stationarity relies on
dividing the questioned epoch into subepochs of the length exceeding
the period of the lowest frequency present in the signal, and then
applying a non-parametric test (e.g. sign test) to statistical
descriptors of these subepochs [18]. Usual length of the
reference epoch does not exceed seconds, so considreing the presence
of low EEG frequencies (order of few Hz) we would have too few
subepochs for a reasonable application of a low-power non-parametric
test
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
-
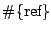 is the
time length of the reference period measured in chosen time widths of
resels.
is the
time length of the reference period measured in chosen time widths of
resels.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ....
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- For the brevity we
omit the distinction between the exact value
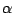 which would be
estimated from all the possible repetitions, and the actually
calculated
which would be
estimated from all the possible repetitions, and the actually
calculated
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... faster.
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- In the pseudo-
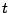 approach we estimate
the distribution of the statistics for the null hypothesis only once
for each frequency (
approach we estimate
the distribution of the statistics for the null hypothesis only once
for each frequency (
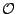
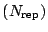 ), and then the test
for each resel is only
), and then the test
for each resel is only
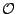
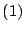 . The full resampling
estimating distributions for each resel is
. The full resampling
estimating distributions for each resel is
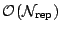
 the number of investigated resels.
the number of investigated resels.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... Internet.
![[*]](file:/usr/share/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.png)
- Playing with different
settings on the two presented datasets involves only changing designated
parameters in configuration files; adapting the system to a different dataset
requires writing a new configuration file. One has to be also aware that the
applied statistical procedures are computer-intensive, therefore in some cases
computations can take up to hours.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.