

Next: The NLO quasilocal functional
Up: Time-dependent density functional theory
Previous: Continuity equation for the
Continuity equation for densities in spin-isospin channels
We can now repeat derivations presented in
Eqs. (21)-(25) by considering the spin-isospin
local-gauge groups, and derive CEs in other spin-isospin channels.
To this end, we first express the nuclear one-body density
matrix (13)-(14)
as a linear combination of nonlocal
spin-isospin densities
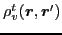 [Carlsson and Dobaczewski(2010)],
[Carlsson and Dobaczewski(2010)],
| |
|
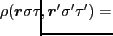 |
|
| |
|
![$\displaystyle \frac{1}{4} \sum_{v=0,1, t=0,1}\left(\sqrt{3}\right)^{v+t}
\left[...
...\sigma'} \left[\tau_{\tau\tau'}^t \rho_v^t(\bm{r},\bm{r}') \right]^0\right]_0
,$](img83.png) |
(28) |
where the sums run over the spin (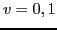 ) and isospin (
) and isospin (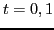 )
indices denoted by subscripts and superscripts, respectively, coupled
to total scalar and isoscalar. Here and below we use the coupling of
spherical tensors both for angular momentum and isospin tensors;
therefore, in Eq. (28) the factor of
)
indices denoted by subscripts and superscripts, respectively, coupled
to total scalar and isoscalar. Here and below we use the coupling of
spherical tensors both for angular momentum and isospin tensors;
therefore, in Eq. (28) the factor of
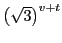 was included so as to cancel the
corresponding values of the Clebsch-Gordan coefficients, and to
maintain the standard normalization of the spin-isospin densities.
The spin-isospin densities can be conversely expressed as the following
traces of the density matrix,
was included so as to cancel the
corresponding values of the Clebsch-Gordan coefficients, and to
maintain the standard normalization of the spin-isospin densities.
The spin-isospin densities can be conversely expressed as the following
traces of the density matrix,
The CEs for densities in the
scalar-isoscalar (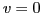 ,
, 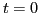 ), scalar-isovector (
), scalar-isovector (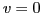 ,
, 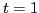 ),
vector-isoscalar (
),
vector-isoscalar (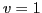 ,
, 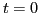 ), and vector-isovector (
), and vector-isovector (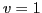 ,
, 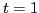 ) channels,
) channels,
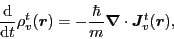 |
(30) |
where
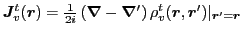 and
and
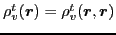 , are now equivalent to the
local gauge invariances, respectively, with respect to the four local
spin-isospin groups:
, are now equivalent to the
local gauge invariances, respectively, with respect to the four local
spin-isospin groups:
Of course, the standard CE derived in Sec. 2.2.1
corresponds to
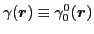 . Note that the
four gauge groups are different:
. Note that the
four gauge groups are different: 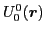 gives the standard
abelian gauge group U(1),
gives the standard
abelian gauge group U(1), 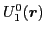 and
and 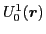 form
the non-abelian gauge groups SU(2), whereas
form
the non-abelian gauge groups SU(2), whereas 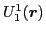 corresponds to the non-abelian gauge group SU(2)
corresponds to the non-abelian gauge group SU(2) SU(2).
SU(2).


Next: The NLO quasilocal functional
Up: Time-dependent density functional theory
Previous: Continuity equation for the
Jacek Dobaczewski
2011-11-11
![]() [Carlsson and Dobaczewski(2010)],
[Carlsson and Dobaczewski(2010)],
![]() ,
, ![]() ), scalar-isovector (
), scalar-isovector (![]() ,
, ![]() ),
vector-isoscalar (
),
vector-isoscalar (![]() ,
, ![]() ), and vector-isovector (
), and vector-isovector (![]() ,
, ![]() ) channels,
) channels,
![]() and
and
![]() , are now equivalent to the
local gauge invariances, respectively, with respect to the four local
spin-isospin groups:
, are now equivalent to the
local gauge invariances, respectively, with respect to the four local
spin-isospin groups: